Windows File Recovery is a popular and free software for recovering permanently deleted or lost files. Learning how to use Windows File Recovery, you can recover the essential files easily and quickly. Follow me!

Windows File Recovery, a free command-line tool developed by Microsoft, is available for Windows 10 version 2004 and later, and enables users to retrieve permanently deleted or lost files from local storage devices, including internal and external hard drives, USB drives, and SD cards.
It uses the Windows File System (NTFS) to recover files, so it's only compatible with NTFS-formatted drives. It can recover a wide range of file types, such as documents, photos, videos, and music files, among others.

Step 1: The software can be downloaded from Microsoft Store. Launch Microsoft Store and type Windows File Recovery in the search bar. (If you cannot launch Microsoft Store, refer to the article Microsoft Store Doesn't Open.)

Step 2: Then click on Get to install it to your computer.

As I mentioned earlier, Windows File Recovery can only recover files or folders on the NTFS file system. For other file systems, like FAT32 file system, you may need to use a third-party tool, such as iSumsoft Data Refixer.
Step 1: After installation, click Open to run the tool.

Step 2: When you are prompted to allow the app to make changes to your device, click Yes.

Step 3: As shown in the panel, the command format is winfr source-drive: destination-drive: [/mode] [/switches]. Additionally, there are two basic modes you can use to recover permanently deleted or lost files: Regular and Extensive, and some sample uses are displayed after you enter the command prompt.
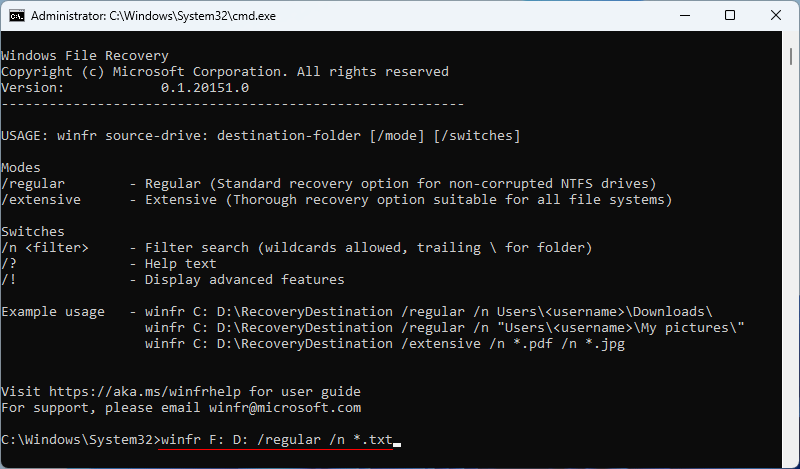
Step 4: For instance, recover all .txt files from F drive to D drive in a regular mode: winfr F: D: /regular /n *.txt.
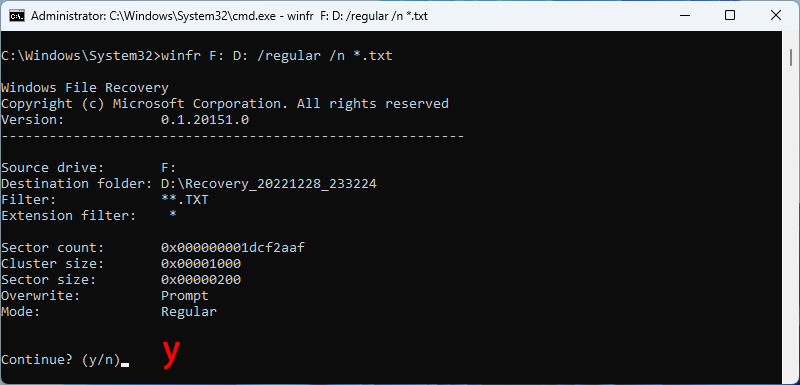
Step 5: When you are asked whether or not to continue, press y to start the recovery operation. Depending on the size of your source drive, this may take a while.
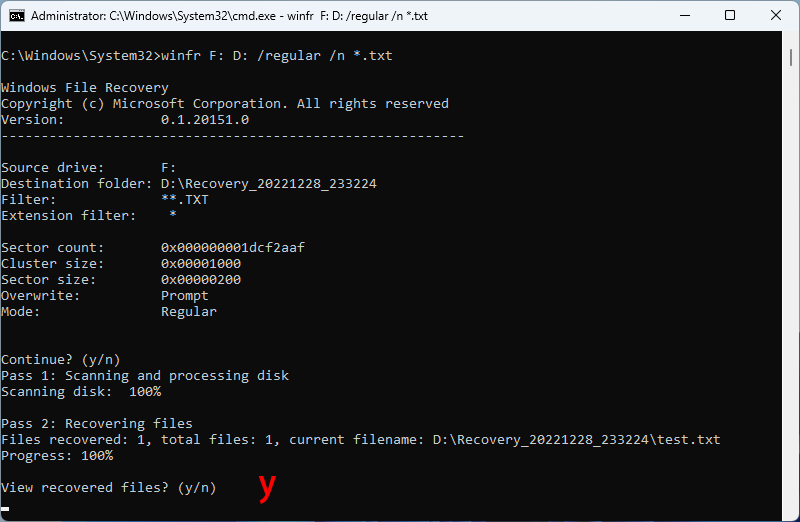
Step 6: When the recovery is complete, you will be asked if you want to view the recovered files. Entering y will automatically take you to the recovery folder.
Recovering deleted files can be a complex and sometimes unpredictable process, and there's no guarantee that all files can be recovered successfully with Windows File Recovery. If a file is unreadable or corrupted after restoring, there could be several reasons for this:
The file was not fully recovered: It's possible that the file was only partially recovered or was damaged during the recovery process. This can happen if the file was fragmented or if there were read errors on the drive. In such cases, you can try running the recovery process again using different recovery options or tools.
The file was overwritten: If the file was deleted a while ago and the drive was used extensively after that, it's possible that the file was overwritten by new data. In such cases, it may be impossible to recover the original file, or the recovered file may be corrupted or incomplete.
The file is in an unsupported format: Windows File Recovery can recover a wide range of file types, but it only supports files in NTFS file system. In such cases, you may need to use a specialized tool or seek professional help to recover the file.
However, by following the best practices and using the right tools and techniques, you can increase your chances of recovering deleted files.