Some people often store important or private folders, files, and data into hard disk. At the meantime, they are also afraid of unauthorized people accessing these important things. So, to protect important data and file security, people tend to use BitLocker to encrypt and maintain disk partitions. However, does drive encryption affect performance?
If so, how much? So anyway, I'm going to test for you to resolve your problem.Tips 1: Different encryption algorithms supported by BitLocker
BitLocker supports AES 128-bit and 256-bit encryption algorithms. By the way, the longer the key, the higher the security, the more difficult it is to break through, but the longer the key is, the longer it takes to encrypt and decrypt the data.
By default, BitLocker in Windows 7 is encrypted using AES 128-bit with Diffuser and Windows 10 encryption is XTS-AES 128-bit.
In this article, we test different algorithms on SSD and HDD to show BitLocker XTS-AES 128 vs. 256 performance.
However, which algorithm to use, and whether to use diffuser, you can open Local Group Policy Editor and navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption. In the right panel, double-click on "Choose drive encryption method and cipher strength" to select the encryption algorithms you want to change.
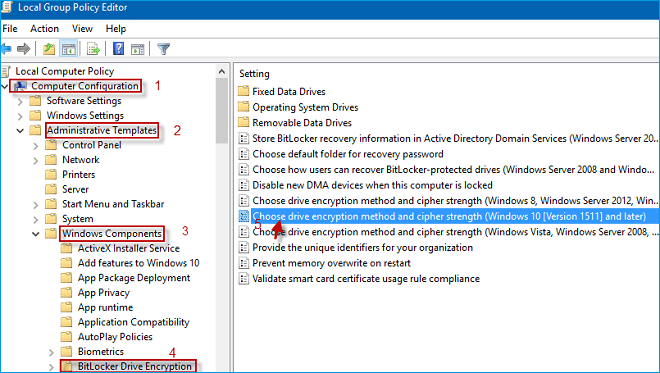
Tips 2: Encryption and non-encryption
You can test the read and write speed in unencrypted situations before encrypting.
Using BitLocker to encrypt hard drive you want to test, and when your hard drive is encrypted, you can test the read and write speed of the encryption.
Let's get down to business. Because all of my partitions of the hard disk have been encrypted completed by BitLocker before, I intend to use the Windows 10 E dish on desktop computer and Windows 10 D dish on laptop as test target, using ATTO Disk Benchmark to respectively test the SSD/HDD read and write performance of the encrypted and unencrypted. Please look closely at the following two tests:
Test 1: SSD with bitLocker VS SSD without BitLocker
Test 2: HDD with bitLocker VS HDD without BitLocker
Note: In these two tests, we used two different versions to test respectively just because of the different time and equipment and there is few effect on the test result.
Testing tool: ATTO Disk Benchmark.
Encryption methods: 1. non-encryption; 2. XTS-AES 128-bit (Default); 3. XTS-AES 256-bit.
SSD: TOSHIBA Q200EX, with 240G storage capacity, SATA3 port.
Processor: Intel Core i5-2430M CPU frequency 2.40GHz, the biggest Turbo frequency is 3.0G, dual-core four-threaded, 3MB cache.
Windows system: Windows 10 Enterprise 64-bit operating system, 1703 version.
1. Does BitLocker slow down SSD? As the comparison below, different BitLocker encryption algorithms have a little impact on SSD read and write performance.
Note: Individual data may be abnormal, which is not our primary concern. And, what we need to pay attention to is the general performance.


2. The following statistical tables show the performance gap before and after encryption intuitively. (The top table shows write speed while the below one shows read speed)


Testing tool: ATTO Disk Benchmark.
Encryption methods: 1. non-encryption; 2. AES-CBC 128-bit; 3. AES-CBC 256-bit.
HDD: SEAGATE Barracuda with 1TB capacity and 7200rpm, the specific type is ST1000DM010, 64MB cache.
Processor: Intel Pentium CPU G4400, dual-core dual-threaded, 3MB cache, clocked at 3.3GHz. The specification of CPU lists the technology that supports the AES New Instructions.
Windows system: Windows 10 Enterprise, 64-bit, 1709 version.
1. As the following pictures show, different BitLocker encryption algorithms both have a certain degree of influence on the write and read speed of the HDD.
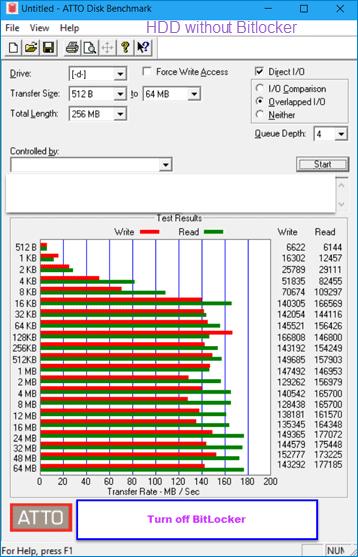
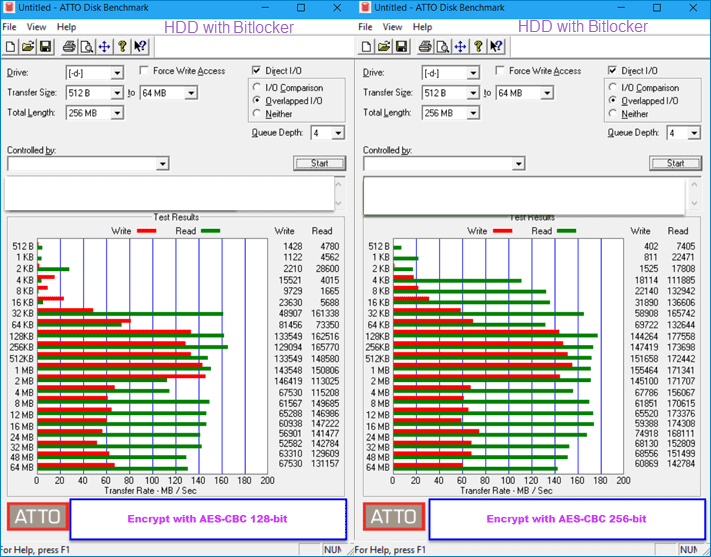
2. The following statistical tables show the performance gap before and after encryption intuitively. (The top table shows write speed while the below one shows read speed)


As can be seen from the results, after encrypting HDD/SSD with different encryption methods, and then testing the encrypted and unencrypted disks, the testing results have obvious differences.
In test 1, the performance loss of writing is less than 1%, the read performance loss is less than 5%.
In test 2, there is not a very large impact on reading performance of HDD, but there are obvious differences when writing data, and the writing performance has a loss of 50% - 62%.