DNS cache is a temporary database that restores domains and IP records and allows your operating system or browser to quickly parse the URL; however, too much DNS cache can lead to DNS cache poisoning, a malicious cyber-attack. Therefore, you may want to clear DNS cache. Here is how to clear DNS caches for Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Windows, MacOS, and Linux.
The Domain Name System (DNS) cache is a temporary database that serves to store information about prior DNS lookups. At the time of each website visit, the operating system and web browser retain a record of that domain and its corresponding Internet Protocol (IP) address. This process eliminates the necessity for repeated queries to a remote DNS server and permits the operating system or browser to rapidly resolve the URL associated with a particular website.
Pros in DNS Cache:
Cons of too much DNS Cache:
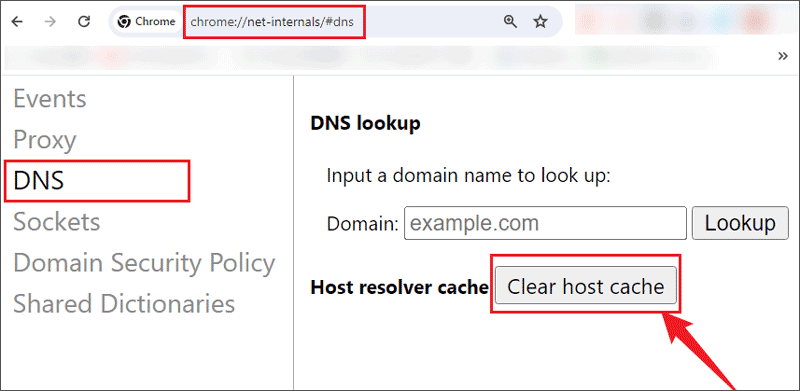
To clear DNS cache on Chrome browser, you can try the following steps:
Step 1: Open Chrome and copy "chrome://net-internals/#dns" to the address bar;
Step 2: Choose the DNS tab and click Clear host cache;
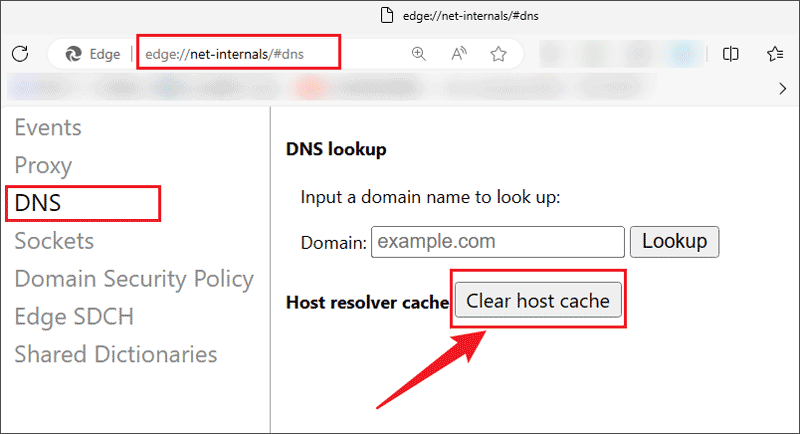
Clear DNS cache on Edge browser is almost the same as Google Chrome browser, check the following steps:
Step 1: Open the Microsoft Edge browser and type "edge://net-internals/#dns" into the address bar;
Step 2: Select the DNS tab and click Clear host cache;
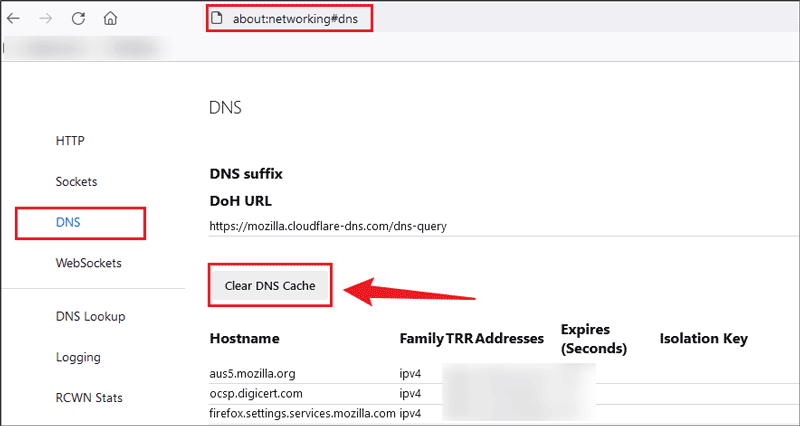
Let me show you how to flush DNS cache on Mozilla Firefox:
Step 1: Turn on the Firefox browser and copy "about:networking#dns" to the address bar;
Step 2: Click Clear DNS Cache;
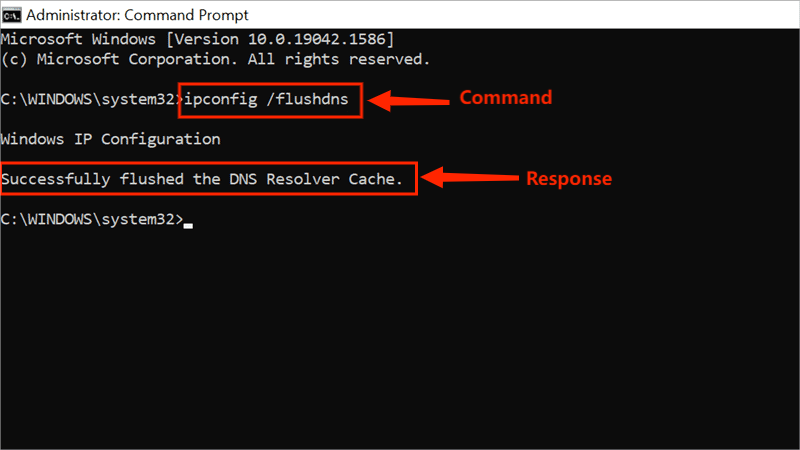
Step 1: Press "Win + R" to open the Windows Command run box;
Step 2: Type "cmd" and press "Ctrl + Shift + Enter" to run as administrator;
Step 3: Type "ipconfig /flushdns" and hit the Enter button;
Step 4: When the DNS has been flushed on Windows, you will receive a message saying "Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache".
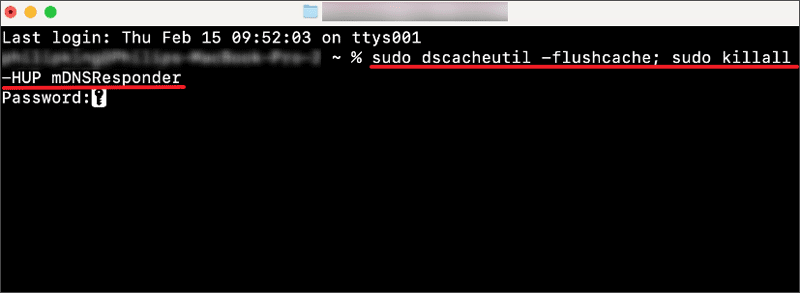
Step 1: Click Finder > Applications > Utilities > Open Terminal window and type the flushing command;
Step 2: The command will be different depending on your Mac version, you can refer to the corresponding command below.
Step 3: Enter the Admin password to run the command;
Step 1: Press "Ctrl + Alt + T" to open Terminal windows;
Different Linux distributions may use different DNS resolvers and caching services (like systemd-resolved, dnsmasq, and NSCD), so specific commands may vary.
Step 2: Type the specific command according to the DNS services;
For Systemd-Resolved: sudo systemd-resolve --flush-caches
For Dnsmasq: sudo service dnsmasq restart
For NSCD: sudo service nscd restart
Q1: Why do I need to clear DNS cache?
1. Clearing DNS cache forces you to re-query the latest DNS information.
2. Clearing DNS cache helps your computer get new DNS records.
3. Clearing the DNS cache helps prevent cyberattacks.
4. Periodically refreshing the DNS cache ensures that your network requests are always based on the latest DNS records.
Q2: How to flush DNS cache in Apple Safari?
Step 1: Open Safari browser > Settings > Advanced;
Step 2: Tick "Show features for web developers";
Step 3: Choose Develop tab > Empty Caches;
Q3: How to know which macOS is using?
Click the Apple menu icon in the desktop > Select About This Mac, then you can find the macOS version.;